COVID-19 Vaccine
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to reduce the risks of COVID-19 infection for both you and your baby. The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), along with other pregnancy experts, including the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American Academy of Pediatrics, recommends that women who are pregnant, breastfeeding, trying to get pregnant now, or may become pregnant in the future be vaccinated against COVID-19.
-
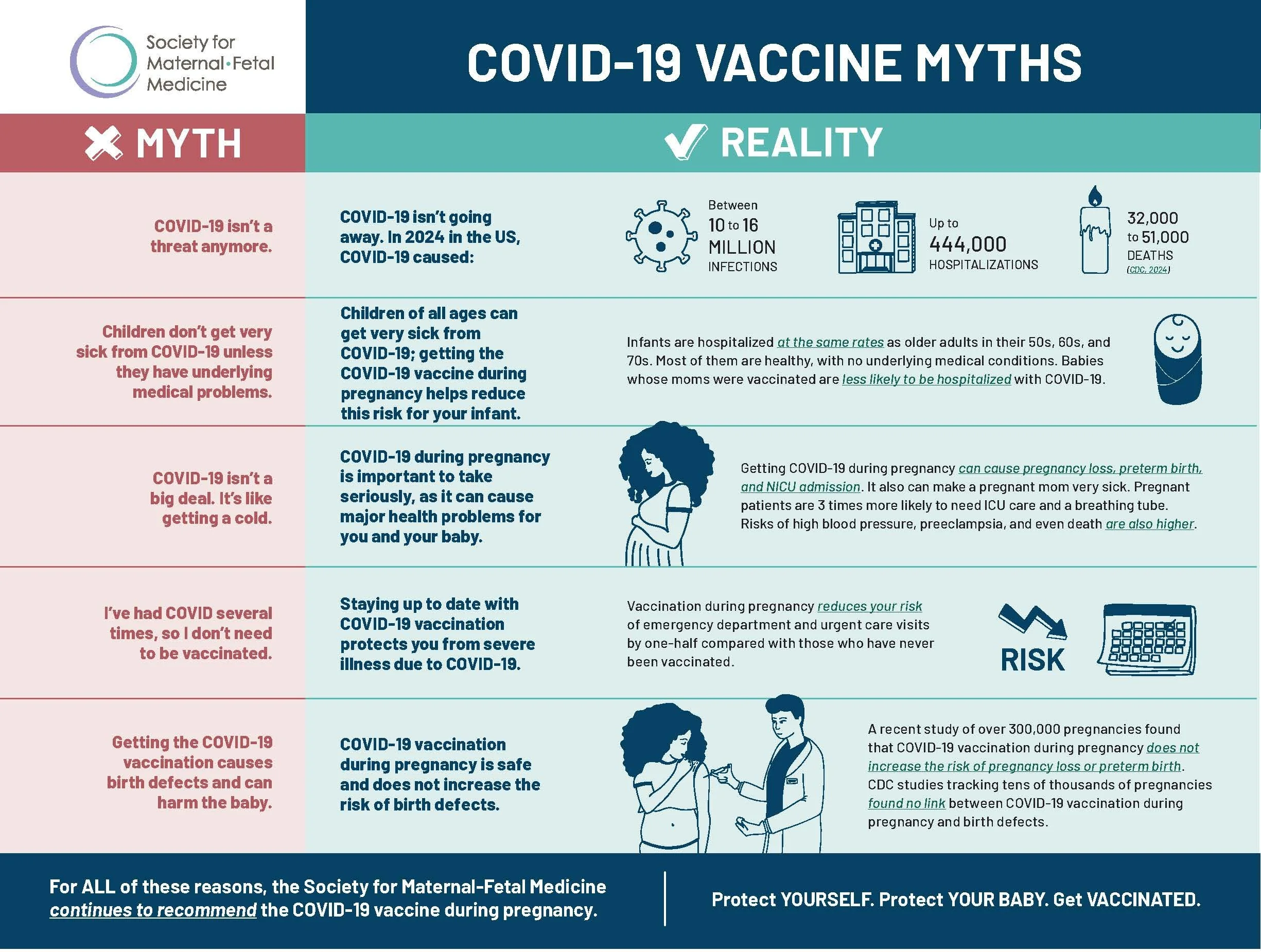
Although most pregnant women with COVID-19 have only a mild illness, about 1 in 10 will develop severe illness. Compared with those who aren’t pregnant, pregnant women infected by the COVID-19 virus:
Are 3 times more likely to need ICU care
Are 2 to 3 times more likely to need advanced life support and a breathing tube
Have a small increased risk of dying due to COVID-19
COVID-19 infection may also increase the risk of pregnancy complications, including stillbirth and preterm birth.
Data show that older pregnant women and those with preexisting health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disorders, have an especially increased risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19.
-
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, consider talking with your healthcare professional about the vaccine. Here are some key points to think about:
The Vaccines Work
COVID-19 vaccines have been shown repeatedly to help protect from severe illness, hospitalization, and death if you get infected with COVID-19.
Getting Vaccinated Helps Protect Your Baby
Getting the vaccine while pregnant helps your immune system create anti-COVID-19 antibodies, which then pass to your baby through the placenta. These antibodies protect your baby from severe COVID-19 illness and hospitalization until they can be vaccinated at age 6 months.
The Vaccines Don’t Cross the Placenta or Affect Future Fertility
The current COVID-19 vaccines are not live vaccines. The vaccines do not cross the placenta because they are quickly broken down by the muscle where they’re given. Remember—the vaccine helps your body make protective antibodies, which do cross the placenta and help protect your baby after they’re born.
There is no evidence that vaccines affect future fertility or causes major changes to the menstrual cycle.
-
You can get vaccinated at any time during pregnancy. Getting the COVID-19 initial dose or booster doses has not been shown to increase the risk of pregnancy loss or miscarriage. The following information shows the available vaccines and the recommended doses you should have in 2024-2025 based on your COVID-19 vaccination history:
If you have NEVER had a COVID-19 vaccine:
| Vaccine: | Number of doses to get in 2025-2026 | Wait time between doses |
|---|---|---|
| Moderna, OR | 1 | N/A |
| Pfizer, OR | 1 | N/A |
| Novavax (for ages 12 and older only) | 2 | 3-8 weeks between doses 1 and 2 |
If you have previously received 1 or more doses of a COVID-19 vaccine:
| Vaccine: | Number of doses to get in 2025-2026 | Wait time between doses |
|---|---|---|
| Moderna, OR | 1 | 8 weeks or more after last dose |
| Pfizer, OR | 1 | 8 weeks or more after last dose |
| Novavax (for ages 12 and older only) | 1 | 8 weeks or more after last dose |
-
Side effects may occur with the first 3 days after getting vaccinated and are generally mild and well-tolerated. These include mild to moderate fever, headache, and muscle aches. Side effects may be worse after the second dose of the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Fever should be avoided during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is recommended if you’ve gotten the vaccine and developed a fever. This medication is safe during pregnancy and does not affect how the vaccine works.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration monitor the safety of vaccines. You can help this effort by signing up for V-safe, a program that monitors people who’ve been vaccinated. No unexpected pregnancy or fetal problems have occurred. There have been no reports of any increased risk of pregnancy loss, growth problems, or birth defects.
Protect Your Family with COVID Vaccination
In English
En Español
Myths vs Reality on Covid-19 Vaccine and Pregnancy
Quick Facts
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy decreases the risk of severe illness for both mother and baby.
Getting the vaccine while pregnant helps your body create antibodies against the COVID-19 virus, which then pass to the fetus. These antibodies protect your baby from severe COVID-19 illness and hospitalization until they can be vaccinated at age 6 months.
Vaccines do not cross the placenta, do not increase risk for miscarriage, and do not affect fertility or cause major changes to the menstrual cycle.
You can get the COVID-19 vaccine at any time during pregnancy.
The COVID-19 vaccine can cause mild side effects, like fever or headache. Acetaminophen is safe to use if needed.
CDC: COVID-19 Vaccination for Women Who Are Pregnant or Breastfeeding
CDC: COVID-19 Vaccination for Women Who Would Like to Have a Baby
MothertoBaby: COVID-19 Subunit Vaccine (Novavax)
MothertoBaby: COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine (Moderna/Spikevax® and Pfizer/Comirnaty®)
Glossary
Antibodies: Proteins made by the immune system in response to a foreign substance, such as a virus.
Immune system: The cells and organs that protect the body against foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
Placenta: A special organ that develops during pregnancy. It allows the transfer of nutrients, antibodies, and oxygen to the fetus. It also makes hormones that sustain the pregnancy.
Last Updated: August 2025